Structure-borne sound
Sound is caused by vibrations which transmit through a medium and reach the ear or some other form of detecting device. Sound is measured in loudness (decibels (dB)) and frequency (Hertz (Hz)).
Sound in the built environment tends to be structure-borne or airborne.
Building Regulations Approved Document E - 'Resistance to the passage of sound' describes structure-borne sound as, ‘...sound that is carried via the structure of a building’. Structure-borne sound results from an impact on, or a vibration against, a part of a building fabric resulting in sound being radiated from an adjacent vibrating surface. A typical example of structure-borne sound is footsteps on a floor which can be heard in a room below.
Structure-borne sound comprises five processes:
- Generation – the source of an oscillation.
- Transmission – the transfer of oscillatory energy from the source to the structure.
- Propagation – the distribution of energy throughout the structural system.
- Attenuation - when waves moving through structures encounter structural or material changes they can be partially reflected which reduces the energy transmitted, and so attenuates the sound.
- Radiation – the emission of sound from an exposed surface.
Structure-borne sound and airborne sound are sometimes considered to be separate entities but they are closely related. Structural vibrations may radiate from surfaces, creating airborne sound, and airborne sound may cause an element of the building fabric to vibrate when it encounters a surface.
Structure-borne sound can be reduced by:
- Carpets and pads.
- Resilient underlay – which can have a similar effect to carpets and pads. Generally, they are made from recycled rubber, rigid fibreglass, foam or other such materials.
- Resilient mounts, sound clips or spring ceiling hangers.
- Soundproofing compounds. Typically the compound is applied between two rigid materials, such as subflooring. The compound dissipates the vibrations caused by sound waves as they move through the structure.
- A suspended ceiling system, raised floor or secondary wall structure.
- High mass constructions that include cavities or offset constructions to prevent transmission of vibrations.
Careful consideration must be given to structure-borne sound when designing buildings. However, the nature of structure-borne sound varies significantly depending on the source of the vibration, the composition of the structure through which it transmits, the radiating surface and the character of the receiving space. This is a complex subject and the design of sensitive spaces such as recording studios can benefit from the advice of an acoustic consultant.
Building Regulations Approved Document E - 'Resistance to the passage of sound' sets minimum standards for impact sound insulation. Impact sound transmission is typically measured in-situ with a tapping machine which uses steel-faced hammers to strike a test surface and generate sound in an adjacent space which can be recorded or monitored. This is useful only in giving an indication of the likely level of impact sound as it does not accurately represent the variety of impacts that might be experienced in practice.
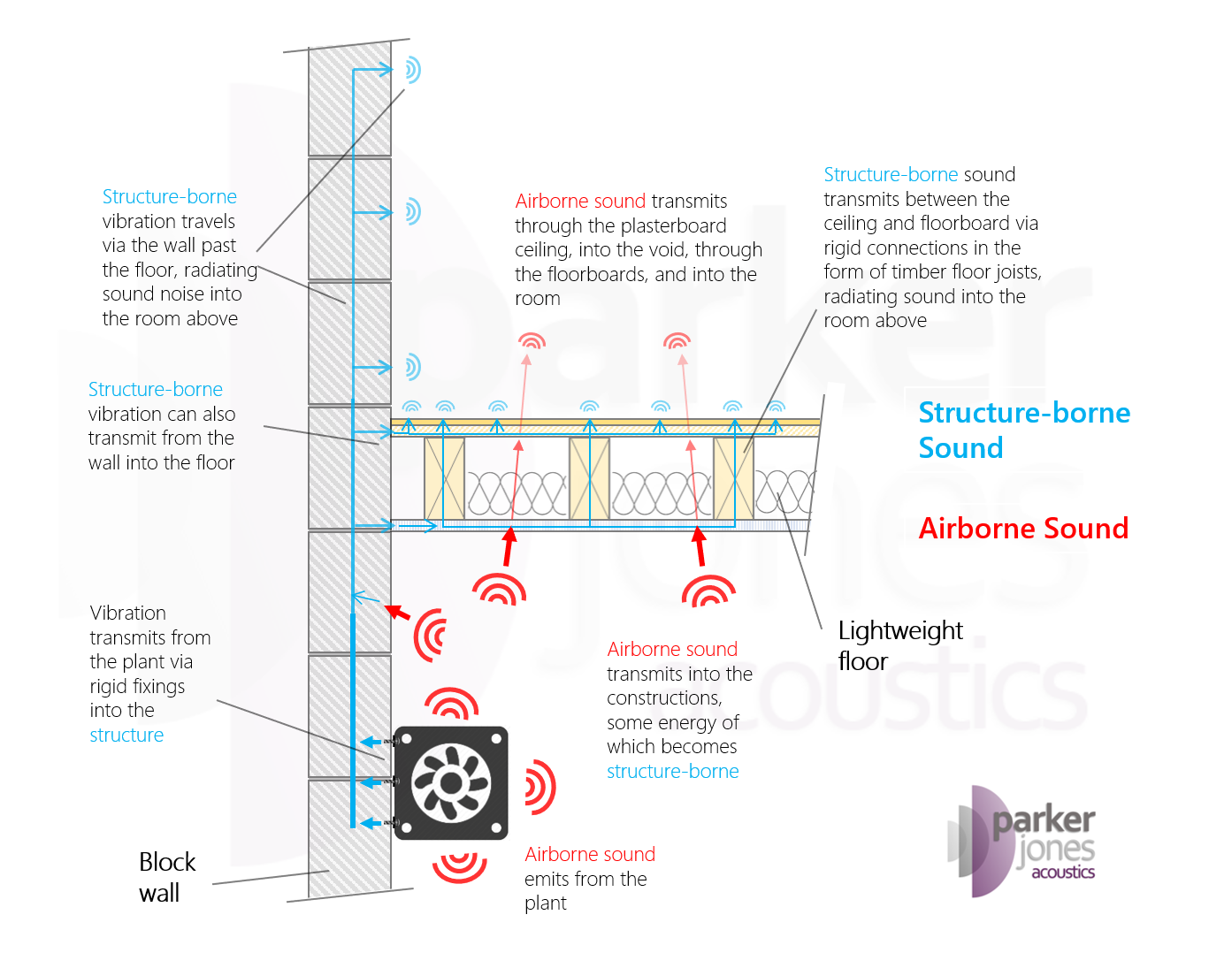
The diagram below provides an example of structure-borne noise paths compared to airborne noise paths, for an item of mechanical plant, transmitting sound into a room above. (Credit: ParkerJones Acoustics)
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Acoustic design for health and wellbeing.
- Acoustics.
- Acoustics in the workplace.
- Airborne sound.
- Approved Document E.
- Ash deafening.
- Building acoustics.
- Building Bulletin 93: acoustic design of schools.
- Building regulations.
- Decibel.
- Impact sound.
- Flanking sound.
- Noise nuisance.
- Pre-completion sound testing.
- Reverberation time.
- Robust details certification scheme.
- Sound absorption.
- Sound frequency.
- Sound insulation.
- Sound reduction index (SRI).
- Sound v noise.
- Underlay.
Featured articles and news
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.
Cutting carbon, cost and risk in estate management
Lessons from Cardiff Met’s “Halve the Half” initiative.
Inspiring the next generation to fulfil an electrified future
Technical Manager at ECA on the importance of engagement between industry and education.
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
Environmental compliance; a checklist for 2026
Legislative changes, policy shifts, phased rollouts, and compliance updates to be aware of.